
Estimate relative growth rate from estimated prevalence
Source:R/estimator-sgolay-growth-rate.R
growth_rate_from_prevalence.RdThis assumes a prevalence that is logit-normally distributed. The exponential growth rate is the first derivative of the mu parameters of this logit-normal. On the link scale these are normally distributed. This function assumes that the time series incidence estimates are uncorrelated to estimate the error in the growth rate, which is a conservative approach resulting in more uncertainty in growth rate than might be possible through other methods. This is all based on Savitsky-Golay filters applied to the normally distributed logit-proportion estimates.
Arguments
- d
a modelled proportion estimate - a dataframe with columns:
time (ggoutbreak::time_period + group_unique) - A (usually complete) set of singular observations per unit time as a `time_period`
prevalence.0.025 (proportion) - lower confidence limit of prevalence (true scale)
prevalence.0.5 (proportion) - median estimate of prevalence (true scale)
prevalence.0.975 (proportion) - upper confidence limit of prevalence (true scale)
Any grouping allowed.
- window
the width of the Savitsky-Golay filter - must be odd
- deg
the polynomial degree of the filter
Value
the timeseries with growth rate columns: A dataframe containing the following columns:
time (ggoutbreak::time_period + group_unique) - A (usually complete) set of singular observations per unit time as a
time_periodproportion.fit (double) - an estimate of the proportion on a logit scale
proportion.se.fit (positive_double) - the standard error of proportion estimate on a logit scale
proportion.0.025 (proportion) - lower confidence limit of proportion (true scale)
proportion.0.5 (proportion) - median estimate of proportion (true scale)
proportion.0.975 (proportion) - upper confidence limit of proportion (true scale)
relative.growth.fit (double) - an estimate of the relative growth rate
relative.growth.se.fit (positive_double) - the standard error the relative growth rate
relative.growth.0.025 (double) - lower confidence limit of the relative growth rate
relative.growth.0.5 (double) - median estimate of the relative growth rate
relative.growth.0.975 (double) - upper confidence limit of the relative growth rate
Any grouping allowed.
Examples
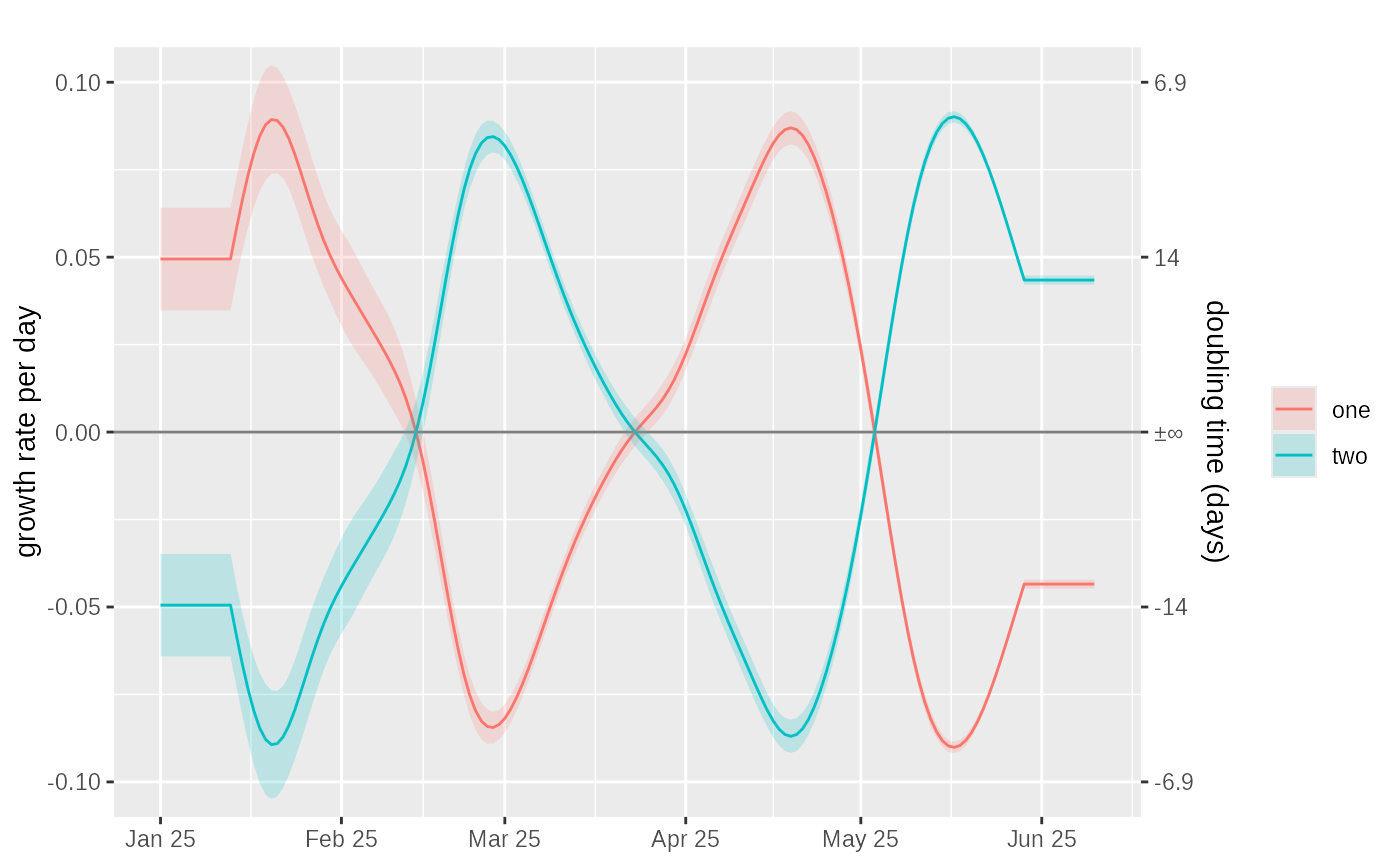
data = example_poisson_rt_2class()
tmp = data %>%
proportion_glm_model(window=7,deg=2) %>%
dplyr::select(time, dplyr::starts_with("proportion")) %>%
dplyr::rename_with(~ gsub("proportion","prevalence",.x)) %>%
dplyr::select(-prevalence.fit, -prevalence.se.fit)
#> Adding missing grouping variables: `class`
tmp = tmp %>%
growth_rate_from_prevalence(window = 25, deg=1)
plot_growth_rate(
tmp,
date_labels="%b %y"
)
 data1 = ukc19::ons_infection_survey %>%
dplyr::filter(name=="England") %>%
timeseries(count=FALSE)
tmp2 = data1 %>%
growth_rate_from_prevalence(window = 25, deg=1)
if(interactive()) {
plot_growth_rate(
tmp2,
date_labels="%b %y",
mapping = ggplot2::aes(colour=name),
events = ukc19::timeline
)
}
data1 = ukc19::ons_infection_survey %>%
dplyr::filter(name=="England") %>%
timeseries(count=FALSE)
tmp2 = data1 %>%
growth_rate_from_prevalence(window = 25, deg=1)
if(interactive()) {
plot_growth_rate(
tmp2,
date_labels="%b %y",
mapping = ggplot2::aes(colour=name),
events = ukc19::timeline
)
}